This information is current as of the date of original publication or update. It may have changed by the time you read this. I invite you to fact-check what you read here.
Please do not use this information for diagnosis or treatment purposes. Before making health decisions, discuss with your physician or other qualified healthcare provider.
I think I am officially “older”. I qualify for Medicare and have reached my full retirement age. I receive the senior discount at restaurants. I remember many events that younger people have only heard about.
I find many advantages to having reached this age and in this article from KFF Health News I learned about more. The vaccines I have received to prevent infections may also protect me from cardiovascular disease and dementia.
I’m sharing this information with you here now, courtesy of KFF Health News.
Vaccines Are Helping Older People More Than We Knew
by Paula Span, January 14, 2026
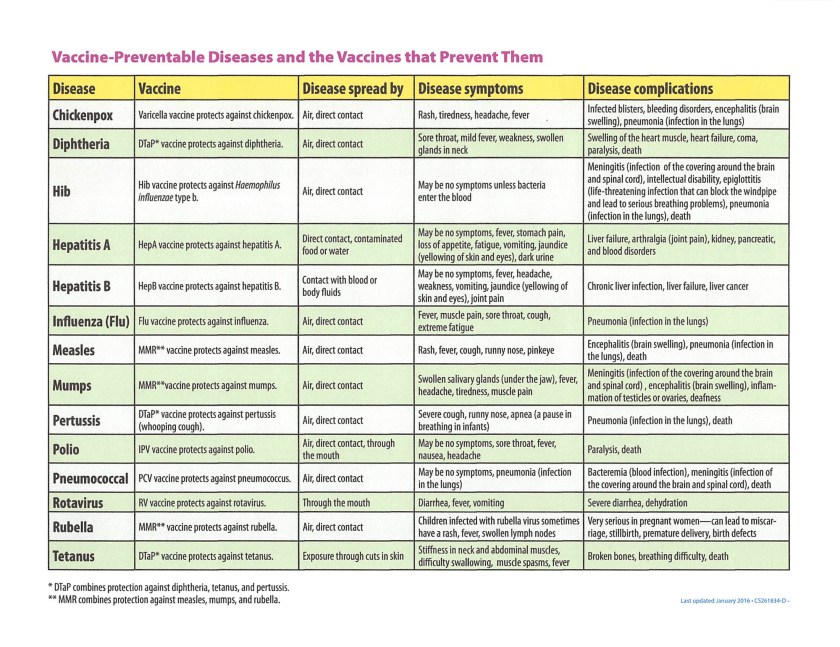
Let’s be clear: The primary reason to be vaccinated against shingles is that two shots provide at least 90% protection against a painful, blistering disease that a third of Americans will suffer in their lifetimes, one that can cause lingering nerve pain and other nasty long-term consequences.
The most important reason for older adults to be vaccinated against the respiratory infection RSV is that their risk of being hospitalized with it declines by almost 70% in the year they get the shot, and by nearly 60% over two years.
And the main reason to roll up a sleeve for an annual flu, influenza, shot is that when people do get infected, it also reliably reduces the severity of illness. However, its effectiveness varies by how well scientists have predicted which strain of influenza shows up.

Off-Target Benefits
But other reasons for older people to be vaccinated are emerging. They are known, in doctor-speak, as off-target benefits, meaning that the shots do good things beyond preventing the diseases they were designed to avert.
The list of off-target benefits is lengthening as “the research has accumulated and accelerated over the last 10 years,” said William Schaffner, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee.
Some of these protections have been established by years of data; others are the subjects of more recent research, and the payoff is not yet as clear. The first RSV vaccines, for example, became available only in 2023.
Still, the findings “are really very consistent,” said Stefania Maggi, a geriatrician and senior fellow at the Institute of Neuroscience at the National Research Council in Padua, Italy.
She is the lead author of a recent meta-analysis, published in the British journal Age and Ageing, that found reduced risks of dementia after vaccination for an array of diseases. Given those “downstream effects,” she said, “vaccines are key tools to promote healthy aging and prevent physical and cognitive decline.”
I rolled up my sleeve for a COVID vaccination.
Yet too many older adults, whose weakening immune systems and high rates of chronic illness put them at higher risk of infectious diseases, have not taken advantage of vaccination.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported last week that about 31% of older adults had not yet received a flu shot. Only about 41% of adults 75 and older had ever been vaccinated against RSV, or respiratory syncytial virus, and about a third of seniors had received the most recent COVID-19 vaccine.
The CDC recommends the one-and-done pneumococcal vaccine for adults 50 and older. An analysis in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, however, estimated that from 2022, when new guidelines were issued, through 2024, only about 12% of those 67 to 74 received it, and about 8% of those 75 and older. (The pneumoccal vaccine protects against disease from the bacteria Streptococcus pneumonia. )
Benefit for Heart Disease Prevention
The strongest evidence for off-target benefits, dating back 25 years, shows reduced cardiovascular risk following flu shots.
Healthy older adults vaccinated against flu have substantially lower risks of hospitalization for heart failure, as well as for pneumonia and other respiratory infections. Vaccination against influenza has also been associated with lower risks of heart attack and stroke.
Moreover, many of these studies predate the more potent flu vaccines now recommended for older adults.
Could the RSV vaccine, protective against another respiratory illness, have similar cardiovascular effects? A recent large Danish study of older adults found a nearly 10% decline in cardiorespiratory hospitalizations — involving the heart and lungs — among the vaccinated versus a control group, a significant decrease.
Lowered rates of cardiovascular hospitalizations and stroke did not reach statistical significance, however. That may reflect a short follow-up period or inadequate diagnostic testing, cautioned Helen Chu, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Washington and co-author of an accompanying editorial in JAMA.
“I don’t think RSV behaves differently from flu,” Chu said. “It’s just too early to have the information for RSV, but I think it will show the same effect, maybe even more so.”
Possible Dementia Prevention?
Probably the most provocative findings concern vaccination against shingles, aka herpes zoster. Researchers made headlines last year when they documented an association between shingles vaccination and lower rates of dementia — even with the less effective vaccine that has since been replaced by Shingrix, approved in 2017.
Nearly all studies of off-target benefits are observational, because scientists cannot ethically withhold a safe, effective vaccine from a control group whose members could then become infected with the disease.
That means such studies are subject to “healthy volunteer bias,” because vaccinated patients may also practice other healthy habits, differentiating them from those not vaccinated.
Although researchers try to control for a variety of potentially confounding differences, from age and sex to health and education, “we can only say there’s a strong association, not a cause and effect,” Maggi said.
But Stanford researchers seized on a natural experiment in Wales in 2013, when the first shingles vaccine, Zostavax, became available to older people who had not yet turned 80. Anyone who was 80 and older was ineligible.
Over seven years, dementia rates in participants who had been eligible for vaccination declined by 20% — even though only half had actually received the vaccine — compared with those who narrowly missed the cutoff.
“There are no reasons people born one week before were different from those born a few days later,” Maggi said. Studies in Australia and the United States have also found reductions in the odds of dementia following shingles shots.
In fact, in the meta-analysis Maggi and her team published, several other childhood and adult vaccinations appeared to have such effects.
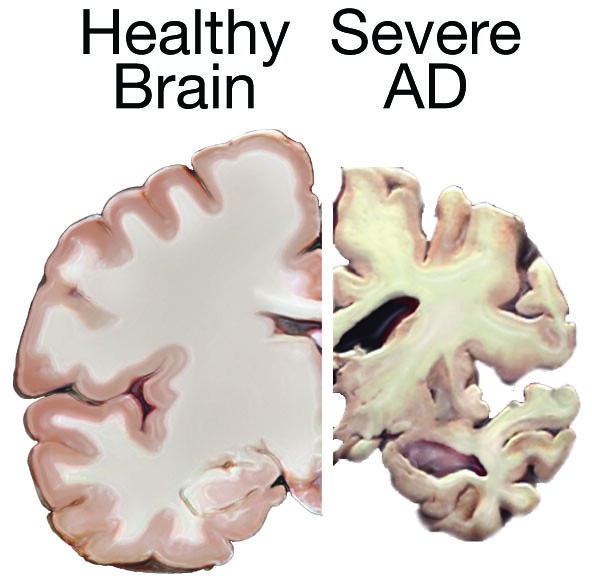
“We now know that many infections are associated with the onset of dementia, both Alzheimer’s and vascular,” she said.
In 21 studies involving more than 104 million participants in Europe, Asia, and North America, vaccination against shingles was associated with a 24% reduction in the risk of developing dementia. Flu vaccination was linked to a 13% reduction. Those vaccinated against pneumococcal disease had a 36% reduction in Alzheimer’s risk.
The Tdap vaccine against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (whooping cough) is recommended for adults every 10 years, with vaccination among older adults often prompted by the birth of a grandchild, who cannot be fully vaccinated for months. It was associated with a one-third decline in dementia.
Other researchers are investigating the effects of shingles vaccination on heart attacks and stroke and of COVID vaccination on cancer survival.
Preventing Damage from Chronic Inflammation
What causes such vaccine bonuses? Most hypotheses focus on the inflammation that arises when the immune system mobilizes to fight off an infection. “You have damage to the surrounding environment in the body, and that takes time to calm down,” Chu said.
The effects of inflammation can far outlast the initial illness. It may allow other infections to take hold, or cause heart attacks and strokes when clots form in narrowed blood vessels. “If you prevent the infection, you prevent this other damage,” Chu said.
Hospitalization itself, during which older patients can become deconditioned or develop delirium, is a risk factor for dementia, among other health problems. Vaccines that reduce hospitalization might therefore delay or ward off cognitive decline.
Will Anti-Vaccine Public Policy Cause Missed Vaccinations in Adults?
Health officials in the Trump administration have assailed childhood vaccines more than adult ones, but their vocal opposition may be contributing to inadequate vaccination among older Americans, too.
Many will not only miss out on the emerging off-target benefits but will remain vulnerable to the diseases the vaccines prevent or diminish.
“The current national policy on vaccination is at best uncertain, and in instances appears anti-vaccine,” said Schaffner, a former member of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. “All of us in public health are very, very distressed.”
This story also ran in The New York Times
Shared without charge under a Creative Commons License by KFF Health News.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Exploring the HEART of Health
I’d love for you to follow this blog. I share information and inspiration to help you transform challenges into opportunities for learning and growth.
Add your name to the subscribe box to be notified of new posts by email. Click the link to read the post and browse other content. It’s that simple. No spam.
I enjoy seeing who is new to Watercress Words. When you subscribe, I will visit your blog or website. Thanks and see you next time.
Use this search box for related posts on this blog or other topics of interest to you.