Oklahoma, where the wind comes sweepin’ down the plain,
Oklahoma!, by Oscar Hammerstein II
You’ve probably heard my state song. It’s from a famous Broadway musical that was made into a movie, both titled Oklahoma!.
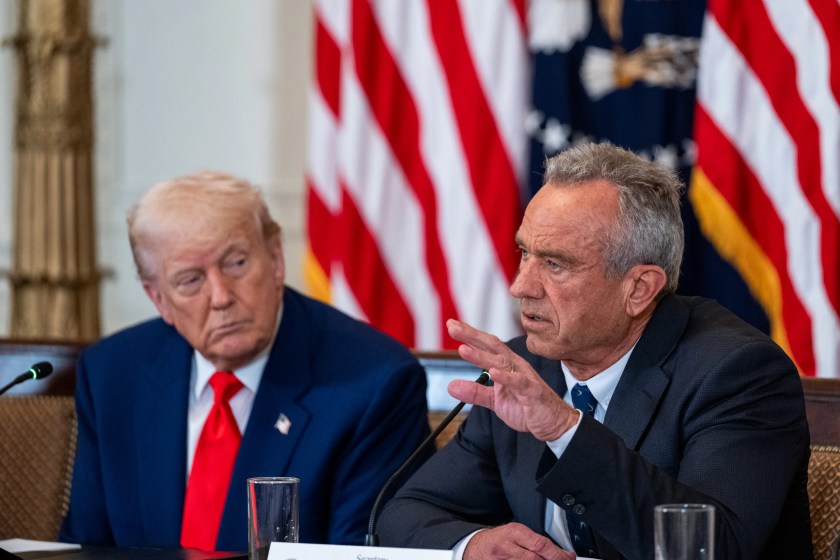
This past week HHS Secretary Robert Kennedy Jr. swept into Oklahoma City to meet with Governor Kevin Stitt to discuss his plan to “Make Oklahoma Healthy Again.” As Secretary, Kennedy’s job is to promote President Trump’s plan to “Make America Healthy Again.”
Maybe he should have scheduled a visit with Oklahoma physicians. They showed up anyway and did not exactly agree with Kennedy’s and Stitt’s priorities-fluoride in the water supply, red food dyes, and how recipients can use SNAP money (food stamps).
I’m sharing an article from Oklahoma Voice about it and what the Oklahoma State Medical Association (OSMA) posted on its website.
You may not live in Oklahoma but something similar is likely to happen in your state if it hasn’t already. I’ll conclude this post with my take on what both sides say.
Governor reveals ‘Make Oklahoma Healthy Again’ plan with RFK for bans on soda, red dye
By: Janelle Stecklein – June 26, 2025 1:57 pm
republished from Oklahoma Voice
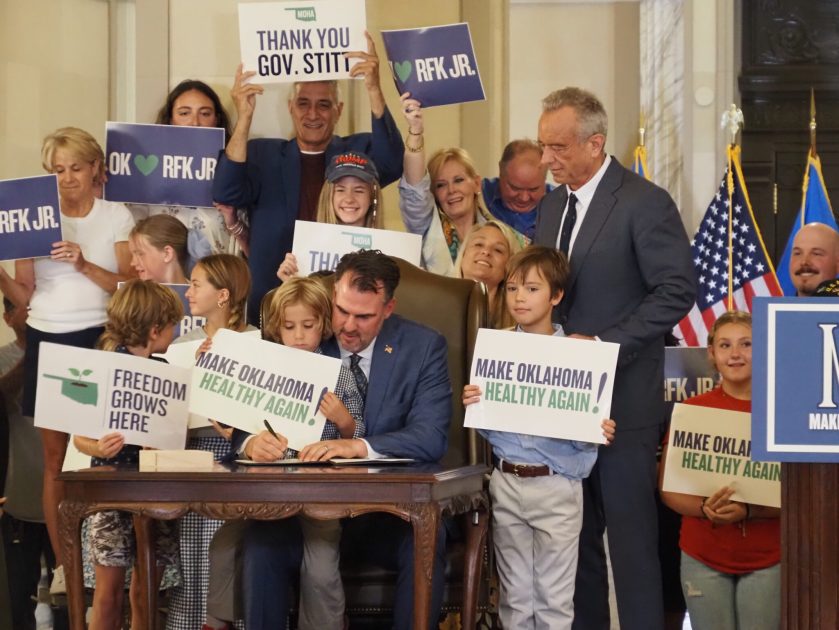
OKLAHOMA CITY — In a move quickly panned by licensed health care providers, Gov. Kevin Stitt announced Thursday that he planned to “Make Oklahoma Healthy Again” by urging state agencies to stop supporting public water fluoridation, removing red food dyes from school and prison meals, and by asking the federal government to approve a request that bans food stamp recipients from purchasing soda and candy.
Stitt’s pledge came minutes after Robert F. Kennedy Jr., the nation’s secretary of Health and Human Services, criticized the state for having the 47th worst health outcomes during a raucous “MOHA” kickoff rally that drew hundreds of people to the state Capitol.

Make Oklahoma Eat Healthy
Oklahoma has become the latest conservative state to submit a waiver to the U.S. Department of Agriculture that seeks to ban the state’s Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program recipients from using their benefits to buy sodas, candies and other confectionery items, Stitt said. Tax dollars will no longer “continue to fund foods that are making people sick,” he said.
State officials will also work with the U.S. Department of Agriculture to find more ways to promote healthy eating and to make food stamp funding go further.
“Eating healthy foods today is going to reduce health care spending and dietary related illnesses later on in life,” Stitt said.
Fluoride and Dyes
The Republican governor also said he’s instructed the Oklahoma State Department of Health to stop recommending fluoride in public water.
“Cities and water districts, they can still choose to do what they want, based on their constituents and the science, but it’s no longer going to be a recommendation for the state health department,” Stitt said.
And Stitt said he’s instructed all state agencies that provide meals to Oklahomans to discontinue their use of artificial dyes. He also plans to convene an advisory counsel to recommend other changes that can improve health outcomes across the state.

Oklahoma’s Physicians Go to OKC
Stitt’s plans immediately faced criticism from licensed medical providers who showed up en masse at the rally, holding signs reading “Support Evidence-Based Health Care”, “Encourage Immunizations,” and “Protect Medicaid.”
Dr. Steven Crawford, chair of the Oklahoma Alliance for Healthy Families, said it would be “disastrous” for children’s health to remove fluoride from water.
“We do know that appropriate public water fluoridation prevents cavities,” he said. “And how do you help children get better nutrition when they don’t have adequate dentition or teeth to be able to eat the food? So I am so sad that the governor is advocating removing appropriate fluoride from public water.”
it would be “disastrous” for children’s health to remove fluoride from water…appropriate public water fluoridation prevents cavities. And how do you help children get better nutrition when they don’t have adequate dentition or teeth to eat the food?
Dr. Steven Crawford, Family Physician,Professor Emeritus,
Senior Associate Dean, Office of Healthcare Innovation and Policy , University of Oklahoma College of Medicine
Crawford said fluoridation of public water and immunizations are two of the major health benefits over the past century and have been critical to improving the state’s and nation’s health outcomes.
He said removing candy and sugary drinks from the list of approved food stamp items isn’t inappropriate, but Stitt neglected to mention that many recipients already don’t get enough resources to buy healthy foods.
The governor also didn’t discuss increasing food stamp funding to ensure children are getting adequate nutrition, particularly during the summer months when they are not eating at school, he said.
Secretary Kennedy avoids vaccine mention
Kennedy, who participated in a staged, ceremonial executive order signing with Stitt, praised the governor’s actions.
“I am so gratified by these actions that are being taken by Gov. Stitt to make Oklahoma healthy again,” Kennedy said.
Spectators heckled Kennedy throughout his speech that focused on America’s soaring rates of obesity, diabetes, and autism, declines in the nation’s fertility rates, and a drop in American teenage boys’ testosterone levels.
Kennedy, who has been criticized as being a vaccine skeptic, did not mention immunizations during his address.
At one point, a state trooper was seen escorting two bystanders from the crowd after one began shouting something unintelligible at Kennedy. A spokesperson for the Oklahoma Highway Patrol did not respond to a request for comment about the encounter.
Kennedy said when people ask him if he’s taking soda and sugary drinks away from Americans, he tells them that they should have the right to drink a bottle of soda.
“We live in a country where we have individual freedom,” he said.
The federal government just should not be paying for it, he said.
“We’re paying for them at the front end by buying soda for the poorest Americans, and then we’re paying for it (on) the back end with this diabetes, for Medicaid and Medicare,” Kennedy said. “And it doesn’t make any sense. We are poisoning the American people.”
He said electing leaders like Stitt will change the way we do things in the U.S. to give American children a better chance of growing up healthy.
This story is republished under Creative Commons license CC BY-NC-ND 4.0.
“Solutions not Slogans” from Oklahoma Doctors
Many of the physicians who attended the event are members of the OSMA, the Oklahoma State Medical Association. (I am a Life Member of the OSMA).
The event was not announced in advance, but with short notice they left their practices for the day to attend the meeting. They also offered their own solutions for “making Oklahoma’s citizens healthy.”
“We agree that Oklahoma’s health needs must be addressed, but we don’t need Washington slogans. We need real solutions and Oklahoma policymakers who are willing to stand up for Oklahoma patients,”
Oklahoma State Medical Association President Sumit Nanda, M.D.

“Primary care is the front line of better health—and that includes science-backed public health efforts like vaccines, preventive care, and chronic disease management.
When we ignore evidence, devalue education, and politicize science, we don’t just fall behind—we fail our people.”
Oklahoma Academy of Family Physicians President Rachel Franklin, M.D., FAAFP
Five Practical Ways to Make Oklahoma Healthy
from the OSMA website
- Invest in health care infrastructure and education by funding hospitals in rural and urban parts of the state, increasing educational opportunities for doctors and dentists, and growing incentives for them to practice in underserved areas.
- Educate Oklahomans about the importance of science-based preventive health care, including wellness visits, dental visits, immunizations, and fluoridation of public water.
- Put Oklahoma tax dollars back in Oklahoma by restoring the DOGE funding cuts to health care.
- Stop insurance company overreach. When insurance companies delay or deny care recommended by a doctor or dentist, patients pay the price.
- Protect Oklahoma’s children and most vulnerable patients by ensuring Medicaid is fully funded.
“where health comes sweepin’down the plain”
These issues and ideas are not unique to Oklahoma. All states need these practical solutions to promote healthy lifestyles and provide optimal medical care when needed.
Contrary to what RFK and others say, physicians are not “keeping patients sick” just to make money. Quite the contrary. Physicians are frustrated because their efforts to prevent illness are often not supported by insurance companies, businesses, the government, and sometimes patients themselves.
Physicians know that food intake plays a major role in promoting health and preventing disease. But trying to micromanage people’s diets by limiting their choices may not be the most efficient and effective way to do so.
Limiting SNAP recipients’ choices seems punitive, not helpful. And I wonder how it will be enforced. What counts as “soda” and what exactly is “candy”? Fruit juice is as high in sugar as soft drinks. Limiting a single source of excess sugar is unlikely to make much difference overall. Perhaps they should provide incentives for buying fresh produce.
The governor didn’t say to ban fluoride in the drinking water, but forbids the state health department from recommending it. If the health department can’t endorse something as basic as fluoride to prevent cavities, then why even exist? And maybe that’s the point.
“Healthcare should be backed by science and carried out by healthcare providers with their patients. Preventive care, immunizations and regular wellness checks are vital in protecting an individual’s health.
Dr. Steven Crawford, Chairman of the Oklahoma Alliance for Healthy Families.
Oklahoma doctors will continue advocating for the health and healthcare of our citizens and I hope the physicians in your area do the same.
Please learn about healthcare issues in your state. Feel inspired to do your part to keep your family and community healthy. I use these sources for state and national healthcare news.
KFF Health News
Health Care-News From The States
Exploring the HEART of Health
Here’s the link to listen to Oklahoma!, my state song.
Oklahoma State Song and Anthem
I’d love for you to follow this blog. I share information and inspiration to help you transform challenges into opportunities for learning and growth.
Add your name to the subscribe box to be notified of new posts by email. Click the link to read the post and browse other content. It’s that simple. No spam.
I enjoy seeing who is new to Watercress Words. When you subscribe, I will visit your blog or website. Thanks and see you next time.
Dr. Aletha
Find my other posts on this topic, or any others you need information about.

You can watch the movie Oklahoma! on Amazon Prime at this link