updated December 10, 2024
I published this post almost 2 months ago. Since then, this issue has become headline news.
The CEO of United Healthcare Insurance Company was shot and killed outside a hotel in New York City. The assailant is a young man who is reported to have expressed anger with the medical insurance industry. New information is unfolding daily.
While I personally and professionally have had issues with insurance companies, nothing in this post should be considered criticism or disparagement of the industry. This post presents an overview of medical debt and what legislators do to address it, not necessarily the causes.
In later posts, I plan to discuss unexpected or excessive medical debt, including how to work with insurance companies and hold them accountable.
Violence is not an acceptable solution and should not be glorified.
the original post
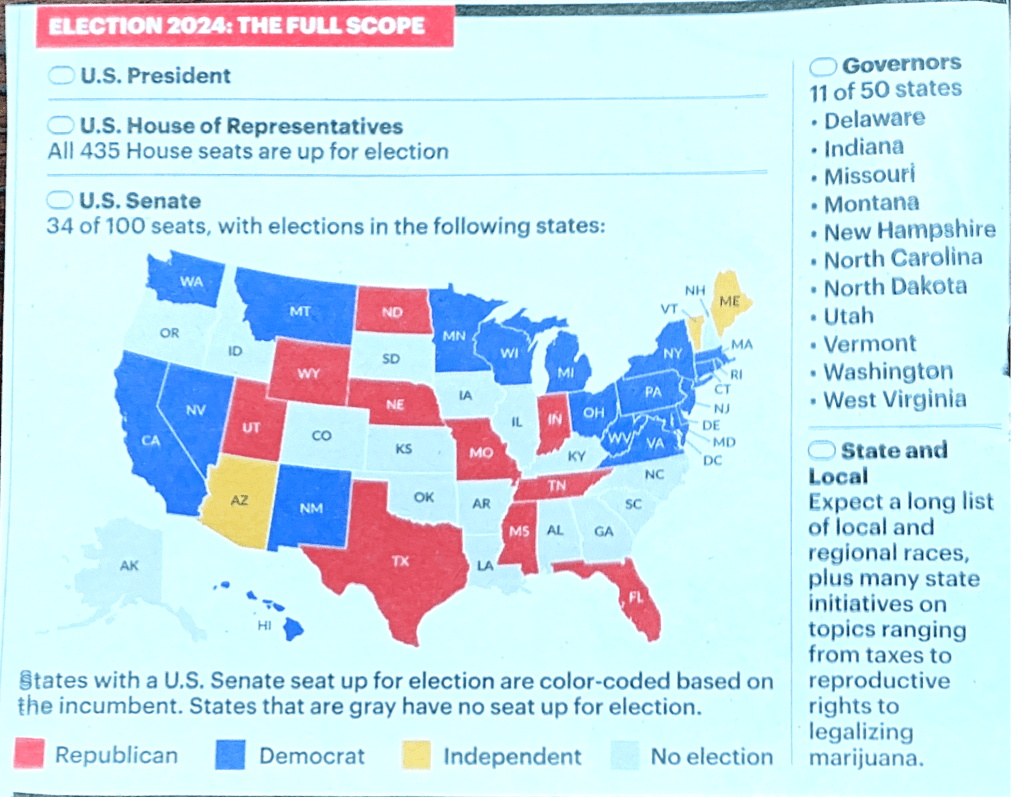
With every election we think it is the most contentious ever, but this year more so. And it’s not just the presidential election that is adversarial, even state and local contests can be vicious.
So it is refreshing to see this report about an issue that some politicians from both major parties agree on, excessive medical debt. Even with good medical insurance, families may owe thousands of dollars on unexpected, unplanned, or catastrophic illnesses.

“About 100 million people in the U.S. are burdened by some form of health care debt, forcing millions to drain savings, take out second mortgages, or cut back on food and other essentials.”
But according to this article, laws have been passed in 20 states since 2021 limiting aggressive hospital billing, and limiting debt collectors.
Efforts to relieve patients from the burden of medical debt have been supported by both Republicans and Democrats and happen in both “red” and “blue” states.
It doesn’t matter if, as a conservative, I’m saying these things, or if Bernie Sanders is saying these things, At the end of the day, it should be all our jobs to advocate for the invisible.
source: Republican Dale Folwell, NC State Treasurer, referencing Vermont’s liberal U.S. senator.
I’ve highlighted some of the key points in this report that I am reprinting by permission from KFF Health News.
Even Political Rivals Agree That Medical Debt Is an Urgent Issue
reprinted by permission from KFF Health News
While hot-button healthcare issues such as abortion and the Affordable Care Act roil the presidential race, Democrats and Republicans in statehouses around the country have been quietly working together to tackle the nation’s medical debt crisis.
New laws to curb aggressive hospital billing, to expand charity care for lower-income patients, and to rein in debt collectors have been enacted in more than 20 states since 2021.
Democrats championed most measures. But the legislative efforts often passed with Republican support. In a few states, GOP lawmakers led the push to expand patient protections.
“Regardless of their party, regardless of their background … any significant medical procedure can place people into bankruptcy,” Florida House Speaker Paul Renner, a conservative Republican, said in an interview. “This is a real issue.”
Renner, who has shepherded controversial measures to curb abortion rights and expand the death penalty in Florida, this year also led an effort to limit when hospitals could send patients to collections. It garnered unanimous support in the Florida Legislature.
Bipartisan measures in other states have gone further, barring unpaid medical bills from consumer credit reports and restricting medical providers from placing liens on patients’ homes.
About 100 million people in the U.S. are burdened by some form of health care debt, forcing millions to drain savings, take out second mortgages, or cut back on food and other essentials, KFF Health News has found. A quarter of those with debt owed more than $5,000 in 2022.
“Republicans in the legislature seem more open to protecting people from medical debt than from other kinds of debt,” said Marceline White, executive director of Economic Action Maryland, which helped lead efforts in that state to stop medical providers from garnishing the wages of low-income patients. That bill drew unanimous support from Democrats and Republicans
“There seems to be broad agreement that you shouldn’t lose your home or your life savings because you got ill,” White said. “That’s just a basic level of fairness.”
Medical debt remains a more polarizing issue in Washington, where the Biden administration has pushed several efforts to tackle the issue, including a proposed rule by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, or CFPB, to bar all medical debt from consumer credit reports.
Vice President Kamala Harris, who is spearheading the administration’s medical debt campaign, has touted the work on the presidential campaign trail while calling for new efforts to retire healthcare debt for millions of Americans.
Former President Donald Trump doesn’t typically talk about medical debt while stumping. But congressional Republicans have blasted the CFPB proposal, which House Financial Services Committee Chairman Patrick McHenry (R-N.C.) called “regulatory overreach.”
Nevertheless, pollster Michael Perry, who has surveyed Americans extensively about health care, said that conservative voters typically wary of government seem to view medical debt through another lens. “I think they feel it’s so stacked against them that they, as patients, don’t really have a voice,” he said. “The partisan divides we normally see just aren’t there.”
When Arizona consumer advocates put a measure on the ballot in 2022 to cap interest rates on medical debt, 72% of voters backed the initiative.
Similarly, nationwide polls have found more than 80% of Republicans and Democrats back limits on medical debt collections and stronger requirements that hospitals provide financial aid to patients.
Perry surfaced something else that may be driving bipartisan interest in medical debt: growing mistrust as health systems get bigger and act more like major corporations. “Hospitals aren’t what they used to be,” he said. “That is making it clear that profit and greed are driving lots of the decision-making.”

Not every state effort to address medical debt has garnered broad bipartisan support.
When Colorado last year became the first state to bar medical debt from residents’ credit reports, just one Republican lawmaker backed the measure. A Minnesota bill that did the same thing this year passed without a single GOP vote.
But elsewhere, similarly tough measures have sailed through.
A 2024 Illinois bill to bar credit reporting for medical debt passed unanimously in the state Senate and cleared the House of Representatives 109-2. In Rhode Island, not a single GOP lawmaker opposed a credit reporting ban.
And when the California Legislature took up a 2021 bill to require hospitals in the state to provide more financial assistance to patients, it passed 72-0 in the state Assembly and 39-0 in the Senate.
Even some conservative states, such as Oklahoma, have taken steps, albeit more modest. A new law there bars medical providers from pursuing patients for debts if the provider has not publicly posted its prices. The measure, signed by the state’s Republican governor, passed unanimously.
New Mexico state Sen. Steve Neville, a Republican who backed legislation to restrict aggressive collections against low-income patients in that state, said he was simply being pragmatic.
“There was not much advantage to spending a lot of time trying to do collections on indigent patients,” Neville said. “If they don’t have the money, they don’t have the money.” Three of 12 GOP senators supported the measure.
North Carolina state Treasurer Dale Folwell, a Republican who as a state legislator spearheaded a 2012 effort to ban same-sex marriage, said all elected officials, no matter their party, should care about what medical debt is doing to patients.
“It doesn’t matter if, as a conservative, I’m saying these things, or if Bernie Sanders is saying these things,” Folwell said, referencing Vermont’s liberal U.S. senator. “At the end of the day, it should be all our jobs to advocate for the invisible.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
What your vote means in 2024
Exploring the HEART of Health
In an upcoming post, I will explain how to avoid and manage excessive medical debt, so please subscribe. For now, if you need help, try this link.
How to get help with medical bills
Please share your experience with medical debt, other readers would benefit from learning how you solved it, or how it continues to affect your life.
I’d love for you to follow this blog. I share information and inspiration to help you transform challenges into opportunities for learning and growth.
Add your name to the subscribe box to be notified of new posts by email. Click the link to read the post and browse other content. It’s that simple. No spam.
I enjoy seeing who is new to Watercress Words. When you subscribe, I will visit your blog or website. Thanks and see you next time.
Dr. Aletha



